- What Are HID Lights?
- Single-ended or Double-ended?
- Ceramic Metal Halides
- Proper HID Lamp Disposal
What Are HID Lights?
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) grow lights are currently some of the best light sources available for indoor horticulture. They offer a superior watt to lumen ratio within the optimal lighting spectrum to provide plants with great indoor lighting for growth and development. Unfortunately, HID lights produce a lot of heat and the indoor area may need to be cooled. These lamps can last a year or longer and the overall efficiency will diminish over time. They also come in several different wattages to accommodate different size indoor growing areas. As a good rule of thumb, the more watts the HID lighting system pulls the more intense the light and heat that is pushed out. HID lights include metal halide and high-pressure sodium lamps that most growers are familiar with, but they also include ceramic metal halides (CMH) or light-emitting ceramic (LEC) lamps as well. Metal halide lamps use a combination of mercury and metal halides to create light through vapor within the arc tube. High-pressure sodium lamps use a combination of xenon, sodium, and mercury to create light through vapor within the arc tube of the lamp. We will discuss CMH lamps differences below.
Single-ended or Double-ended?
Single-ended lamps (also referred to as bulbs) are elongated and almost oval in shape. They are wide which is necessary to house all the inner components and they screw in much like a regular light bulb does, but into a wider socket known as a Mogul base. Inside the HID lamp is an arc tube, a wire frame, and a button getter. The arc tube looks like an opaque inner tube that connects to the base of the lamp and creates light by heating materials inside. The element and materials inside the arc tube determine what color and the level of brightness that is emitted from the lamp. The metal wire frame holds the arc tube in place and provides power. The button getter acts like an air filter inside the lamp to collect any impurities inside, reducing contamination, and providing a longer lamp life. The components of the lamp are cased in what’s known as the outer jacket. The outer jacket is made out of borosilicate or a glass that has a low melting point, while double-ended lamps have an outer jacket made out of quartz which can withstand higher temperatures.
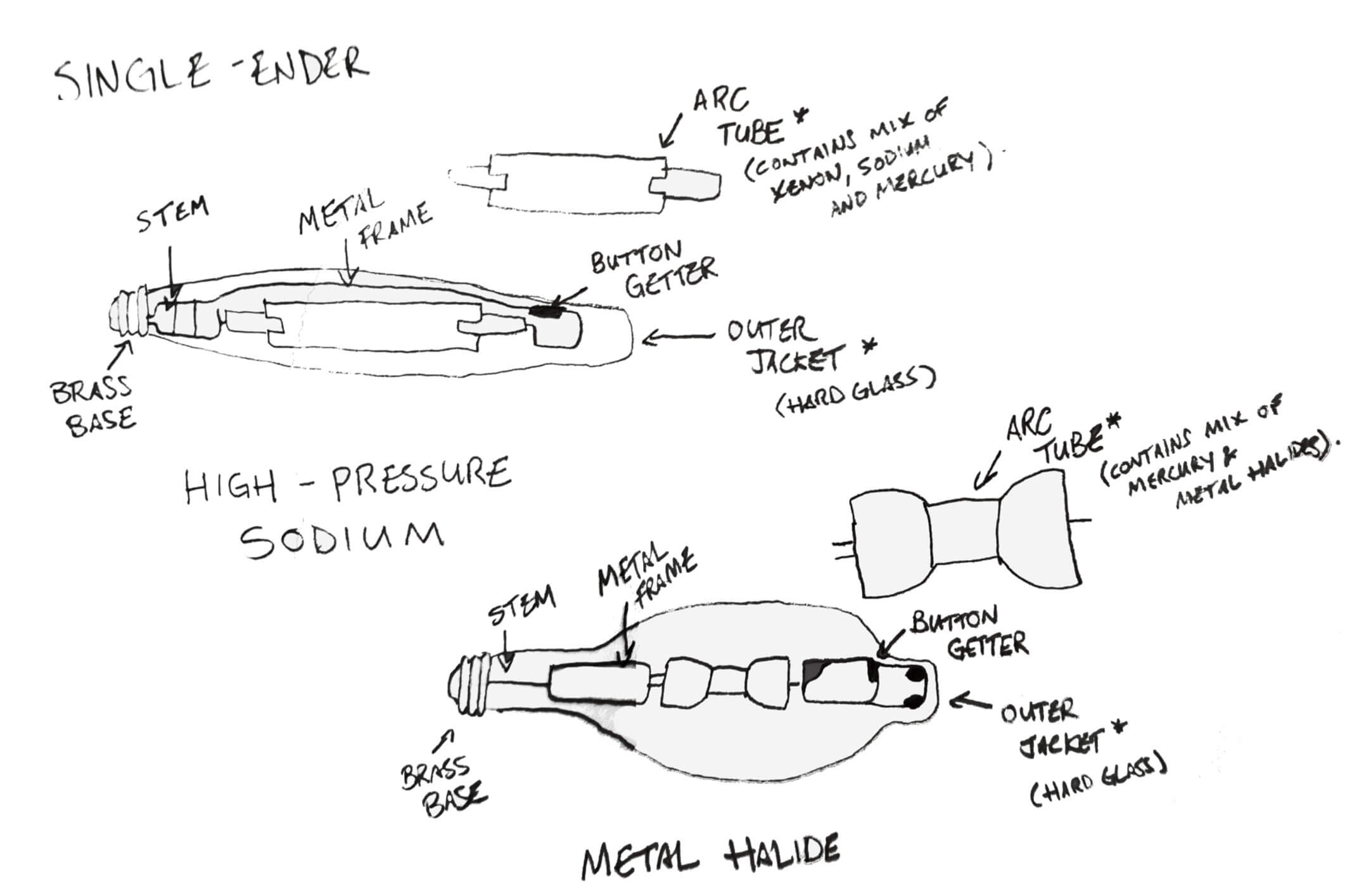
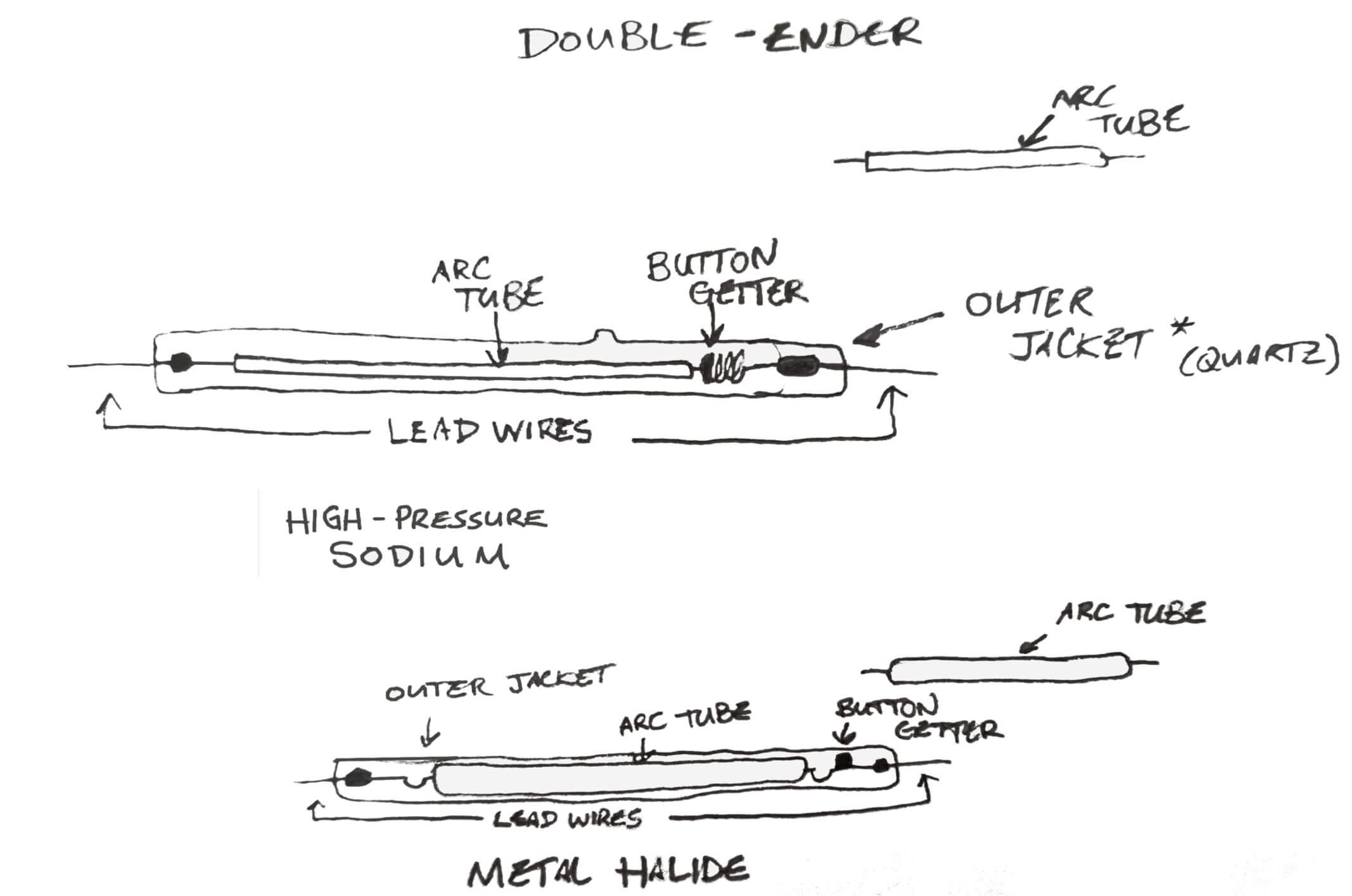
Double-ended bulbs have similar components as single-ended lamps, but the arc tube in a double-ended bulb is smaller and is supported by two lead wires that protrude out both ends of the lamp. Since the lead wires support the arc tube, there is no need for a metal wire frame and the lamp is thinner than single-ended bulbs as a result. The framework of a single-ended lamp hinders the spread and intensity of the light, whereas the framework of a double-ended lamp does not, making them more efficient and reduces degradation. It is estimated that after 10,000 hours of use, double-ended lamps can output up to 90% of their original intensity. Not only this, but because of the superior design, double-ended lamps can have up to 30% in an increase in light intensity and PAR output compared to single-ended lamps. The outer jacket of DE lamps use quartz which can withstand higher temperatures compared to the outer jacket of SE lamps made of borosilicate (a low-melting-point glass).
Ceramic Metal Halides
CMH lamps are also referred to as Light-Emitting Ceramic (LEC) lamps and are considered High-Intensity Discharge lamps. The main difference between a CMH and an MH lamp is that a CMH lamp has an arc tube made of ceramic and an MH lamp has an arc tube made of quartz.
Proper HID Lamp Disposal
HID lamps contain mercury which is considered hazardous to humans and the environment. This is why proper disposal of these lamps is crucial. No matter if you are a home grower or working in a commercial facility, HID lamps need to be collected, properly stored, and taken to a local recycling site that accepts devices containing mercury. There is a government database that tracks recyclable materials and businesses who will accept them known as Earth911. Using the search engine for the database is as easy as entering in a recyclable material and a zip code for location.
Comments powered by Talkyard.