- What is Coco Coir?
- What is Peat Moss?
- Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
- Coco Coir or Peat Moss?
What is Coco Coir?
Coco coir, or coconut coir, is a renewable soil amendment or growing medium that is used in cannabis cultivation. The coir is removed from the coconuts using water to separate the material with certain manufacturers using tidal waters instead of freshwater. If tidal waters are used, then the manufacturer may flush out the salts that are retained by the coir later prior to storing. Once the coir is separated from the coconuts, the coir is dried and organized into bales for aging and storage. The aging phase is important, but can lead to the growth of certain pathogens and pests which is why processing facilities may steam treat the coir. The coconut coir bales are then broken down and processed into the growing medium that is recognizable. These harvesting and processing methods are generally considered more environmentally friendly when compared to peat moss. Although, you can see how the manufacturing process can lead to a contaminated product which is why it is important to choose your source wisely. Coconut coir can be broken down to three different types: fiber, pith (also known as coconut peat), and coco chips. These different types are mixed at different ratios by different processing facilities which can affect the properties of the growing medium.
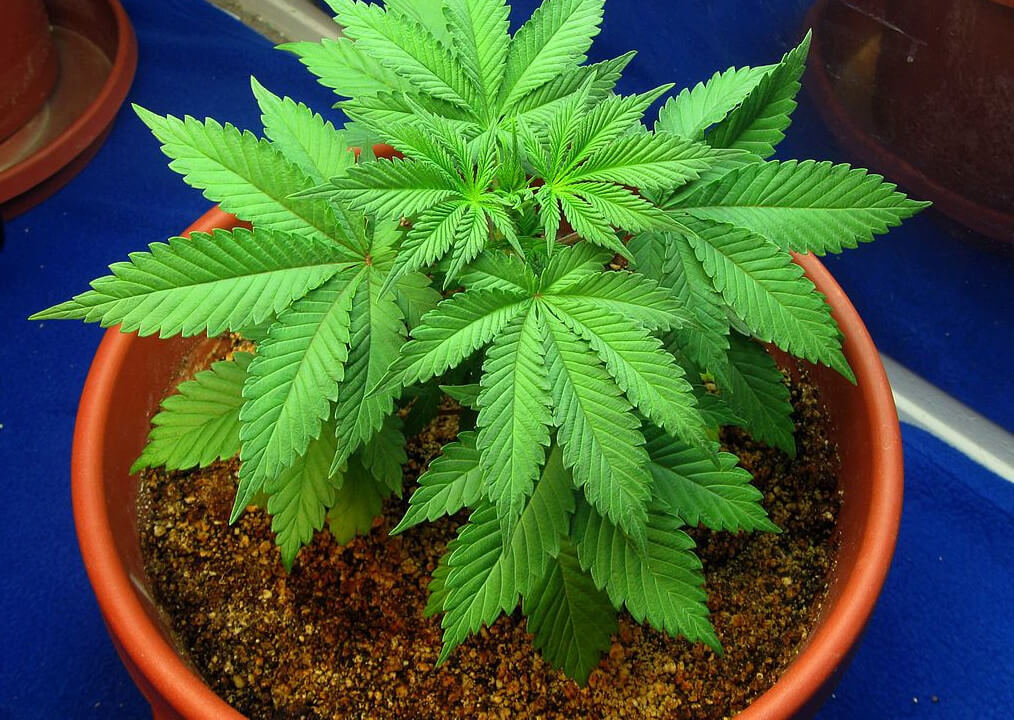

As a growing medium it is pH neutral which is why it does not need limestone added. The properties of coco coir make it less hydrophobic than peat moss, but it naturally has a higher cation exchange capacity (CEC) which is why many growers recommend flushing as part of your watering routine. The growing medium is inert after processing which means that there are no nutrients within it. Instead, when you water the medium you will be adding nutrients. Coco coir is relatively inexpensive when compared to peat moss despite longer shipping routes because shipping over water is cheaper than shipping over land.
| Pros of Coco Coir for Cannabis | Cons of Coco Coir for Cannabis |
|---|---|
| Relatively inexpensive. | Possibly contaminated product from certain manufacturers. |
| Retains moisture well. | Recommended to mix with perlite with ratios around 70% coco 30% perlite to increase aeration and lower CEC. |
| Relatively high CEC which means nutrients do not leach easily from the medium. | Recommended to mix with worm castings to add micronutrients and macronutrients which helps with cannabis growth. |
| Environmentally friendly. |
What is Peat Moss?
Over time, plant materials that are submerged under water in bogs break down to form a type of soil known as peat. The most common is peat from the sphagnum moss plant which can be found in the wetlands of the northern hemisphere including Canada, Russia, and Northern Europe, but peat can also consist of herbaceous or woody vegetation. Canada supplies a majority of the peat moss for the United States and through the Canadian Sphagnum Peat Moss Association (CSPMA), they attempt to restore peatlands and conserve land to make it a sustainable resource. It is estimated that as a country, Canada is harvesting about 1 million tons annually while peatlands are being restored at a rate of 70 million tons of peat in the same amount of time although I could not confirm this information with additional sources. Despite the mission to change how peat moss is viewed, many Northern European countries limit the harvesting of peat due to concerns of depletion and the effects of the environment and opt to use alternatives instead. In fact, the common view of peat moss is that it is not environmentally friendly even if it is a sustainable resource which is why many growers opt to use coco coir instead among other reasons.

Peat moss is naturally hydrophobic and acidic and cannot be stored as long as coco coir which means it is unlikely you will have a contaminated product. Mixes using peat moss usually add perlite, limestone, and a wetting agent in order to combat all of these issues for growers. The perlite helps aerate the mix and provides more of a neutral pH to the medium. The limestone helps buffer the pH which makes it more suitable for cannabis plant growth. Peat moss also contains some micronutrients that are beneficial to cannabis, but in relatively small amounts compared to compost which is why water-soluble nutrients are used.
| Pros of Peat Moss for Cannabis | Cons of Peat Moss for Cannabis |
|---|---|
| Unlikely to be contaminated by pests or pathogens. | Does not store well for long periods of time over 1 year. |
| Contains some micronutrients that are beneficial to the growth of cannabis. | Recommended to mix with limestone to buffer pH as peat moss is naturally acidic. It increases the CEC of the mix which helps prevent leaching of nutrients. |
| Recommended to mix with a wetting agent to make a naturally hydrophobic medium more absorbent. |
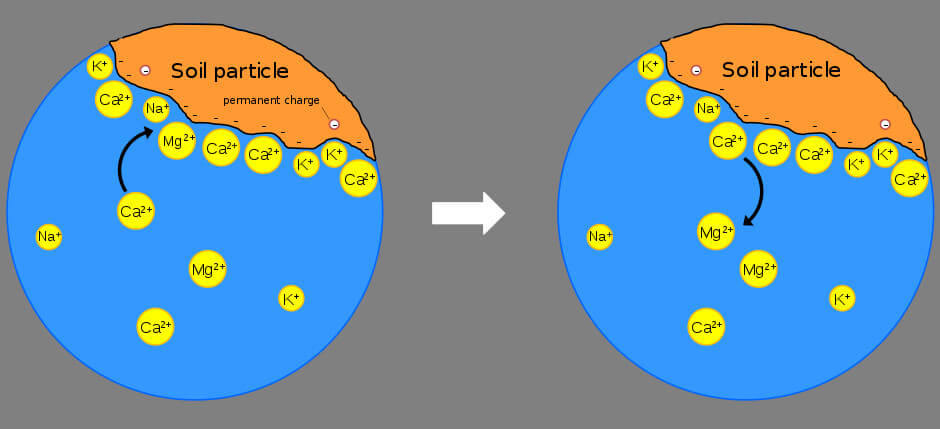
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
Nutrients are composed of elements, some of these elements have an electrical charge which are known as ions. Positively-charged ions are known as cations and negatively-charged ions are known as anions. The most common cations for cannabis cultivation include: calcium (Ca++), magnesium (Mg++), potassium (K+), ammonium (NH4+), hydrogen (H+), and sodium (Na+). The most common anions for cannabis cultivation include: chlorine (Cl-), nitrate (NO3-), sulfate (SO4=), and phosphate (PO43-). The total number of cations a growing medium can hold, otherwise known as its total negative charge, is the cation exchange capacity or CEC. A higher CEC means that the growing medium has a greater negative charge and can hold more cations. This influences the growing medium’s ability to hold onto many essential nutrients over time.
Coco Coir or Peat Moss?
After reading about coconut coir and peat moss growing mediums, it becomes clear that there are differences between the two, but there are a variety of mixes used to create a growing medium more suitable for cannabis plant growth and development. Coconut coir is commonly mixed with worm castings and perlite, while peat moss is commonly mixed with limestone and perlite at different ratios to achieve similar mixes. In the end the resulting mixes are similar, but not the same. It is important to note that coco coir will be cheaper and more environmentally friendly, but the trade-off is you may risk getting a contaminated product when buying coco coir. Using peat moss is commonly viewed as less environmentally friendly and can be relatively more expensive, but the growing medium is more likely to be free of contaminants.
Comments powered by Talkyard.