- What Are Microbial Tests?
- Mycotoxins
- Testing Methods
What Are Microbial Tests?
There are potential health risks for individuals who consume cannabis products contaminated with yeast, mold, salmonella, E. Coli, or mycotoxins. Many states test for these contaminants and Colorado is one of those states that requires both medical and retail cannabis and various cannabis products be tested for yeast, mold and bacteria otherwise known as a microbials test in an effort to protect cannabis consumers from potential health risks due to consumption of contaminants. The microbials test is mandated by the Marijuana Enforcement Division (MED) and looks for:
- Salmonella <1 CFU
- Shiga-Toxin producing E. Coli (STEC) <1 CFU
- Mold <10^4 CFU
- Yeast <10^4 CFU
Salmonella, STEC (Shiga toxin-producing E. Coli), mold, and yeast can all potentially pose adverse health risks to consumers. Symptoms from consumption of contaminated cannabis can appear as wheezing, irritated eyes or skin, and in severe cases it can cause respiratory damage. Retesting is available for any product that fails its initial microbial testing, but the retest requires two new samples be submitted for the procedure in the state of Colorado. Cannabis testing in Colorado has slowly evolved from mandatory potency testing in 2014, to pesticide testing in 2015, microbial testing in 2017, mycotoxin testing in 2019, and finally heavy metals testing in 2020. There are five state certified and ISO-accredited labs in the state of Colorado:
- Gobi Labs, Gobi Analytical in Wheat Ridge, Colorado.
- Agricor Labs in Denver, Colorado.
- Agriscience Labs in Denver, Colorado.
- Aurum Labs in Durango, Colorado.
Mycotoxins
Mycotoxins are toxic metabolites produced by fungi that can colonize on cannabis plants. Since there is no evidence that cannabis flowers harbor significant levels of mycotoxins, it is unlikely that mycotoxins would be identified on cannabis buds or flowers. Instead, tests for mycotoxins focus on cannabis extracts. If the mold/fungi happens to be of a type which produces mycotoxins, those carcinogenic compounds may be concentrated during the extraction process this is why mycotoxin testing is required for cannabis concentrates in Colorado as of 2019.
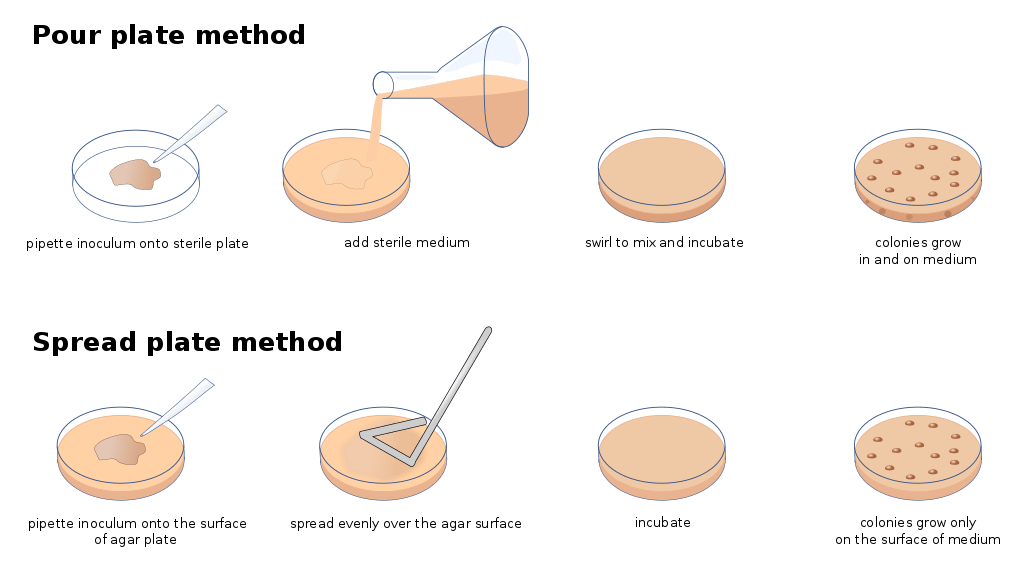
Testing Methods
The Cannabis Inflorescence and Leaf monograph, published by the American Herbal Pharmacopoeia, is the leading literature on microbial testing and many states use it to determine thresholds for microbial testing. The recommendation listed inside is less than 10,000 CFU/g on cannabis plant material and 1,000 CFU/g on extracts. Currently, total yeast and mold tests are conducted using traditional culture plating, while qPCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology is used to test bacteria for analysis. A microbials test can be finished in as little as three days by some labs.
Certain species of yeast and mold could be harmless, but others such as the aspergillus fumigatus, produces toxins that can be toxic to humans. Unfortunately, current microbial tests in Colorado do not differentiate between pathogenic and benign microbes which is why additional testing for mycotoxins is carried out on cannabis extracts.
Comments powered by Talkyard.